Attorney advertisement by Edwin Aiwazian of Lawyers for Justice, P.C., headquartered at 450 N Brand Blvd, Glendale, CA 91203
Workers in California who have been recently laid off or lost their jobs due to unforeseen circumstances may find themselves needing to apply for unemployment benefits in California. The state offers CA unemployment benefits designed to support workers during these challenging times by providing partial wage replacement. Typically, unemployment compensation in California ranges from $40 to $450 per week. However, the exact benefit amount depends on your previous earnings and work history.
While this guide covers important details about eligibility and the benefits system, many unemployed workers may also be victims of wrongful termination and you may be entitled to additional legal protections or compensation. If you believe you were wrongfully terminated, contact Lawyers for Justice, P.C. at (818) JUSTICE for a free consultation.
Basic Eligibility Requirements for Unemployment Benefits in California

Millions of Californians pay into the state’s Unemployment Insurance (UI) system every week, but not every worker qualifies for unemployment benefits. To be approved for unemployment benefits CA, applicants must meet certain criteria related to their work history, income, and legal status.
U.S. Citizenship or Legal Work Authorization
To receive CA unemployment benefits, you must be either a U.S. citizen or legally authorized to work in the United States. The California Employment Development Department (EDD) may require proof of citizenship, a valid work visa, or permanent resident documentation. If your work authorization expires while collecting benefits, your eligibility may end immediately. This requirement ensures unemployment benefits are provided only to individuals legally able to participate in the U.S. labor market.
Unemployed or Reduced Hours Through No Fault of Your Own
You must be unemployed or have reduced working hours through no fault of your own to qualify for benefits. Common qualifying circumstances include layoffs, company downsizing, or position eliminations. In most cases, you will not be eligible if you voluntarily quit without good cause or were fired for serious misconduct. However, if you left your job for legally accepted reasons, such as unsafe working conditions or harassment, you may still be entitled to unemployment benefits.
Sufficient Earnings During the Base Period
Benefits are calculated based on your past earnings during a “base period,” typically the first four of the last five completed calendar quarters before your claim. For example, if you file a claim in July 2025, your base period would be from April 1, 2025, to March 31, 2026. The EDD uses this timeframe to determine your eligibility and calculate your weekly benefit amount. If your earnings were too low or inconsistent during this period, you may not qualify for CA unemployment benefits.
How Long Can You Collect Unemployment Benefits in California?

A common question is, “how long can you collect unemployment in California?” Generally, you can collect benefits for up to 26 weeks within a one-year period. The exact duration depends on your work history and earnings. During periods of economic crisis or federal emergency programs, benefits may be extended beyond 26 weeks. If you’re wondering how long does California unemployment last or how long does CA unemployment last, know that 26 weeks is the typical maximum timeframe for most claimants.
How Much Money Can You Receive? What is the Max Unemployment Benefit in California?
Your weekly benefit amount depends on your previous wages. In California, the minimum is usually $40 per week, while the max unemployment in California is $450 per week. The Employment Development Department calculates your benefit based on wages during your base period. These benefits are intended to partially replace lost income, offering a financial bridge while you search for new employment.
What Situations Affect Your Eligibility for Unemployment Benefits?
Not all workers who lose their jobs automatically qualify for benefits. The EDD reviews the specific circumstances of your job separation carefully. For example, workers laid off due to company downsizing or lack of work typically qualify. However, if you were terminated for misconduct, such as theft or harassment, your claim may be denied. If you quit your job, you must prove you had “good cause” related to California law. For example, unsafe conditions or harassment, to remain eligible.
It is important to keep detailed records of your termination, including any communications or written notices from your employer. These documents can be critical if you need to appeal a denial or prove your case to the EDD.
Common Reasons You May Be Denied Unemployment Benefits in California

- Voluntarily quitting without good cause: Leaving for personal reasons like career change or manager conflicts typically disqualifies you, unless you left due to unsafe work environments or harassment.
- Termination for misconduct: Being fired for serious violations such as theft or repeated insubordination can result in denial.
- Insufficient work history or earnings: Not having enough wages in your base period to qualify.
- Refusing suitable work: Declining reasonable job offers consistent with your skills and wages can stop your benefits.
- Failure to meet ongoing requirements: You must certify your eligibility every two weeks, remain available for work, and actively seek employment.
Benefits are meant for workers who lost their jobs through no fault of their own and who remain ready and willing to work.
What to Do if Your Claim is Denied
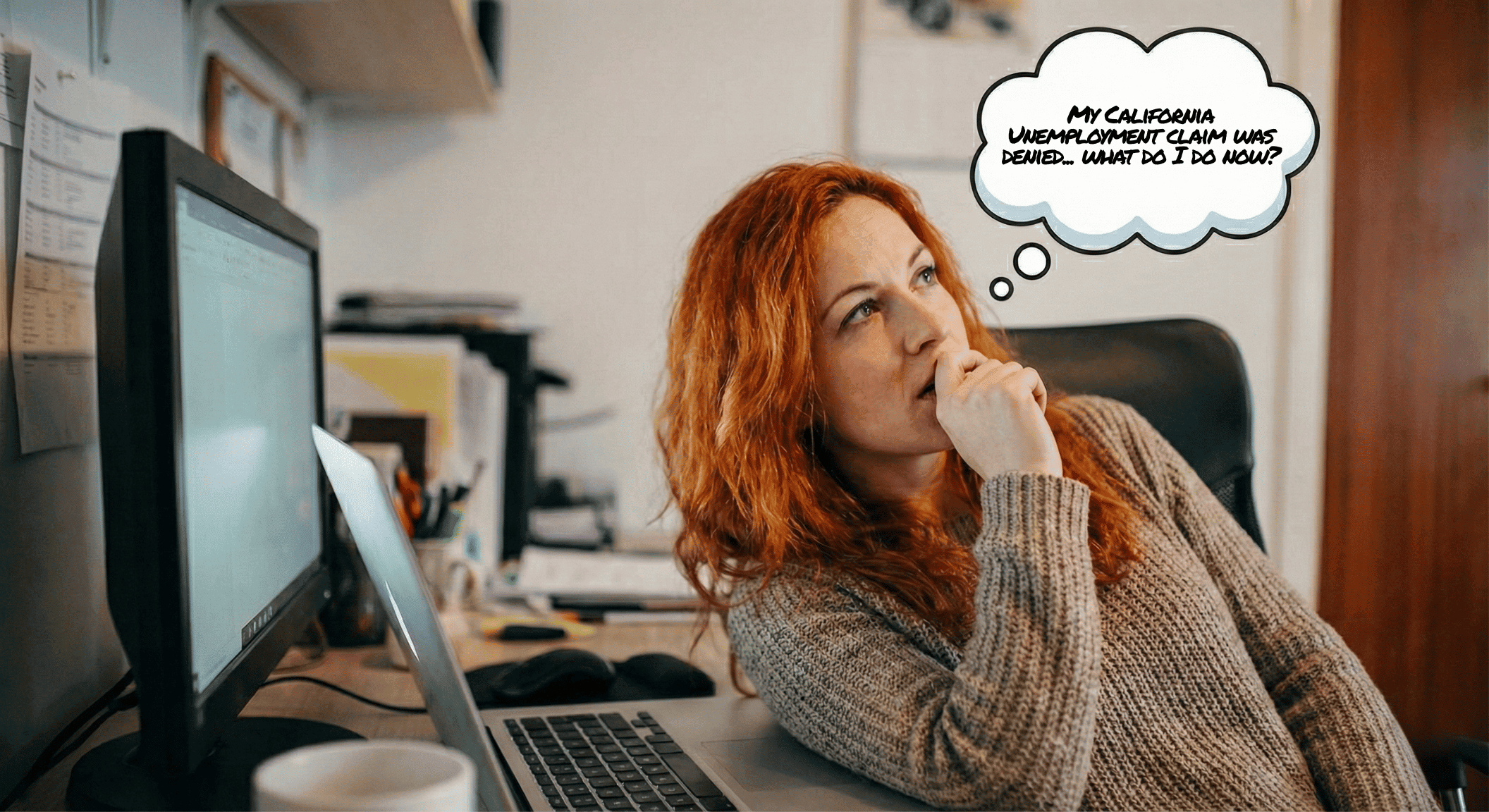

If your unemployment claim is denied, you have the right to appeal. The EDD will send a Notice of Determination explaining the reason. You have 30 days to challenge the decision with the California Unemployment Insurance Appeals Board. There, you can present evidence, testimony, and documentation. Many claimants successfully overturn denials, especially when they clarify misunderstandings that could otherwise cause unnecessary financial hardship.
Working with an experienced employment attorney can make the appeals process easier. Legal guidance helps you understand the denial, gather strong evidence, and present your case clearly at the hearing — improving your chances of securing the benefits you may be entitled to.
When to Contact an Employment Lawyer

If you believe you were wrongfully terminated — fired due to a protected characteristic or unlawful reason — you may be entitled to compensation beyond unemployment benefits. The attorneys at Lawyers for Justice, P.C. have over a decade of experience fighting for workers’ rights and winning compensation for victims of wrongful termination in California. Call (818) JUSTICE for a free consultation and to discuss your legal options.
Unemployment Insurance Benefits in California – FAQ
Q: How long can you collect unemployment in California?
A: Typically, you can collect benefits for up to 26 weeks, with extensions possible during economic downturns or federal emergency programs.
Q: What disqualifies you from unemployment in California?
A: Common disqualifications include voluntarily quitting without good cause, termination for misconduct, insufficient earnings, refusal of suitable work, or failing ongoing eligibility requirements.
Q: How do I apply for unemployment benefits in California?
A: You can apply online via the EDD’s UI Online portal, by phone, or by mailing a paper application.
Q: What is the max unemployment benefit in California?
A: The maximum weekly benefit amount is $450.
Q: Can self-employed workers get unemployment benefits in California?
A: Generally, no, unless special programs or exceptions apply during emergencies.
Q: Can I work part-time and still receive unemployment?
A: Yes, but your benefit amount may be reduced based on your earnings.
Q: Do I have to pay taxes on unemployment benefits?
A: Yes, unemployment benefits are taxable income at the federal level but are not taxed by California state.
Q: How long does it take to start receiving unemployment payments in California?
A: Typically about three weeks, assuming no eligibility issues or complications.
Q: Can my employer contest my unemployment claim?
A: Yes, employers may contest claims if they believe the termination was due to misconduct or you quit without good cause.
Q: Do I need to look for work while receiving unemployment benefits?
A: Yes, claimants generally must actively seek employment and be available for work to maintain eligibility.
Q: Can you get unemployment if you were fired?
A: Yes, if the termination was not for misconduct, you may still qualify.
Contact Lawyers for Justice, P.C. for Help with Unemployment and Wrongful Termination Cases
If you need assistance navigating unemployment benefits in California or believe you were wrongfully terminated, it’s important to get legal advice. The experienced employment lawyers at Lawyers for Justice, P.C. are here to help you understand your rights and fight for the benefits and compensation you may be entitled to. Contact our team by clicking here and filling out a brief contact form, or call us today at (818) JUSTICE for a free consultation.
Disclaimer: This blog is for informational purposes only and does not constitute as legal advice. Each case is unique, and eligibility for unemployment benefits may vary. Please consult with a qualified attorney or the California Employment Development Department for guidance specific to your situation.
Attorney advertisement by Edwin Aiwazian of Lawyers for Justice, P.C., headquartered at 450 N Brand Blvd, Glendale, CA 91203
Think you deserve justice?
-
Get a Free Case Evaluation
-
Retain Service with No Upfront Cost
-
Get the Justice You Deserve
-
No Win, No Pay